U.S. battery storage has jumped from 47 MW in 2010 to 11,071 MW in 2023, according to American Clean Power. Helping commercial and industrial (hereafter C&I) customers understand their energy bills and how battery storage can support improved energy management is more crucial than ever. Whether it's a C&I client seeking to leverage current incentives or enhance energy optimization strategies for operational resiliency, our exploration offers a roadmap for installers to navigate and help their customers capitalize on these energy optimization opportunities.
Battery storage is a potential game-changer for C&I energy management
Battery storage has the potential to transform C&I energy optimization efforts. It allows businesses to store surplus energy, whether generated from sources like solar panels, generators, or the grid and utilize it when needed. Battery storage benefits C&I facilities, which often face high energy demand costs.
For installers speaking with C&I customers, informing them about the potential game-changing benefits of battery storage, including enhanced energy resilience and energy bill cost reductions is crucial. Businesses can use battery storage to lower their electricity expenses by utilizing stored energy during peak demand periods when energy rates are at their highest. The ideal payback period for Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) and solar is less than ten years, depending on their circumstances; this could be longer or shorter depending on the facility’s energy demand. We’ve seen payback periods as short as four years in circumstances where battery storage was implemented to support peak shaving of heavy equipment with inflexible time usage.
The ability to store and manage energy efficiently also means businesses can better control their energy consumption patterns, leading to more predictable operating costs, making it a strategic tool in modern energy management for the C&I sector. To understand the ROI of an ESS for your client’s facilities, it’s essential to look at two facets simultaneously: their energy bills and the incentives particular to their location and circumstances.
Examining C&I energy bills first
C&I clients often face the challenge of deciphering complex electricity bills. These bills differ significantly from residential ones because of additional charges and unique rate schedules. To effectively manage and reduce energy costs, it's essential to understand the following components of C&I electricity billing:
What are demand charges?
Unlike residential bills based mainly on consumption (kWh), C&I clients incur demand charges based on peak electricity usage during a billing cycle. This determines the demand charges applied, usually in dollars per kilowatt (kW) or kilovolt-ampere (kVA).
What is a rate schedule?
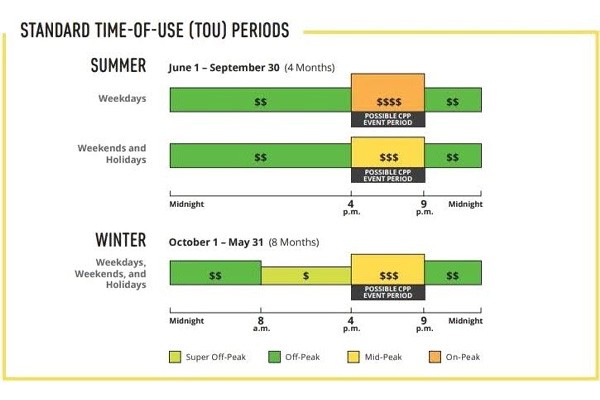
C&I ratepayers are billed according to specific rate schedules, which can significantly influence the total cost. Understanding your business's rate schedule, often denoted by codes (for example., A-1, B-3, TOU-GS-2), is crucial as it impacts the calculation of demand and energy charges. For example, Southern California Edison (SCE) lays out its Business Rate Basics for Small-Sized Business Customers. SCE business customers with demands of 20 kilowatts (kW) or less are eligible for their Rate Schedule TOU-GS-1. Critical Peak Pricing is also an option for business customers, whereby customers can leverage a discount on summer electricity rates in exchange for higher prices during 12 - 15 CPP events per year, based on the following time of use schedule.
How is energy charged?
This component is based on the actual electricity used (measured in kWh). Some businesses are subject to time-of-use (TOU) rates, where costs vary depending on the time of day, making off-peak hours more cost-effective.
What is the Power Factor?
The power factor measures how much power is actually being used to perform useful work, ranging between 0 and 1. A low power factor can lead to penalties and higher costs. A "low power factor utility charge" refers to an additional fee assessed by an electric utility company to customers with a power factor below a certain threshold, typically around 0.95, essentially penalizing them for not efficiently using electricity due to excessive reactive power draw on the grid; this means they are paying for more electricity than they are actually using to perform work. Improving the power factor, possibly through the installation of corrective equipment, can reduce apparent power draw and demand charges.
Managing C&I energy costs
By analyzing the billing components of C&I clients, you can assist them in implementing strategies to control their energy expenses, which may encompass the following:
Implementing peak shavings. Implementing measures to use stored energy can significantly nullify demand charges.
Selecting the appropriate rate schedule. Choosing a rate schedule that aligns with energy consumption patterns to optimize costs.
Improving power factor. Avoid penalties and reduce demand charges by improving the power factor.
Search tool for C&I battery storage incentives
The Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE) is one of the most helpful tools for narrowing down applicable battery storage incentives by jurisdiction, battery chemistry, and other factors. The search is filtered by location, technology, and type of incentive. For example, suppose your client operates a facility in California and purchases qualifying battery storage from Briggs & Stratton. In that case, you can use this system to help them uncover the additional 20% incentive via SGIP.
The business case for battery storage in C&I
For C&I customers, battery storage presents a compelling business case, marked by a blend of cost savings, ROI, and participation in demand response programs. When introducing these benefits to C&I clients, it’s important to discern their particular circumstances and applicable rebates and then articulate the direct impact on their bottom line and operational efficiency to determine battery storage's actual impact and ROI on their facilities. The business case will come from analyzing their current energy bills and crafting a strategy for implementing onsite energy generation and battery storage.
How to discuss incentives with C&I clients
Cost savings and ROI
When discussing energy storage with C&I clients, focus on how it can optimize energy usage and integrate renewable energy sources. This leads to substantial savings on electricity bills, primarily by reducing peak demand charges. Discussing the ROI here is essential, as it involves comparing the upfront costs, including equipment, installation, and operational expenses, against the expected savings over the system’s lifespan. This comparison helps clients understand the financial benefits and the payback period of their investment in energy storage.
Demand response programs
Highlight to customers the financial advantages of participating in demand response programs. Energy storage enables businesses to reduce grid consumption during peak periods.
Backup power and operational resilience
Emphasize the value of energy storage as a source of backup power alongside broader ROI themes, ensuring uninterrupted operations during power outages. This is particularly crucial for businesses that depend on a continuous power supply, such as data centers or manufacturing processes. The operational resilience provided by energy storage systems can be critical for these businesses, safeguarding against losses and ensuring operations continue due to power disruptions.
Incentives for C&I customers
Federal and state tax credits
Discuss the federal investment tax credit (ITC), which, as of 2024, offers a 30% credit for storage systems over 5 kWh in size for commercial properties. It's important to note that this is subject to specific conditions, like prevailing wage requirements. Also, state-specific incentives should be highlighted, using examples such as California’s SGIP, which offers a rebate for installing battery storage. These incentives benefit businesses in high fire-threat districts or with low-income customers.
Rebates and performance-based incentives
Explain to customers how rebates provide a lower upfront investment and can significantly reduce the payback period for battery storage installations. Illustrate to customers a system amortization schedule paired alongside rebates that demonstrate when a commissioned system's costs are levelized.
By effectively communicating these aspects, installers can help C&I customers understand battery energy storage systems' financial and operational benefits, guiding them toward informed decisions that align with their business objectives.

Visit the Briggs & Stratton Residential applications page to talk to an expert and learn more.

Request a Commercial Consultation
Talk with a Briggs & Stratton energy expert by clicking the button below and provide basic information about your upoming project!